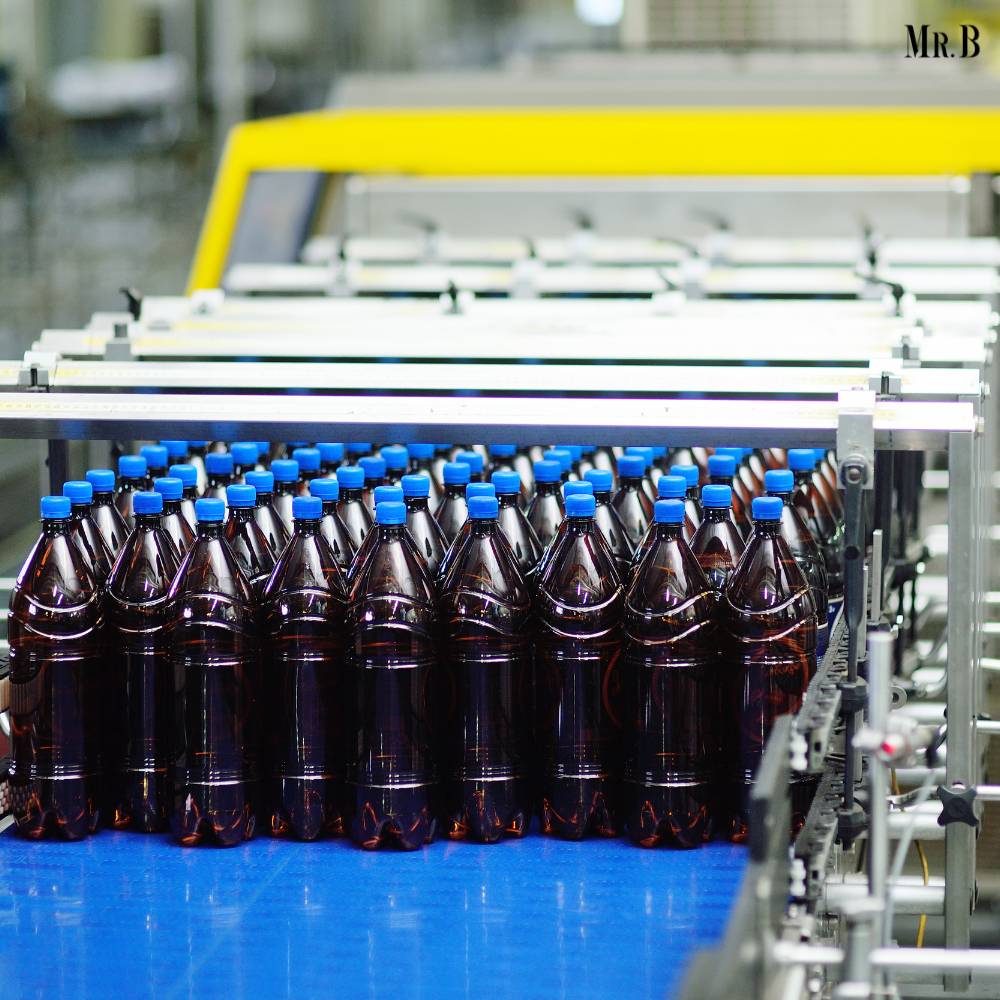
The option of contract manufacturing works better these days in the food and beverages industry. In the ever-evolving world of the food and beverages industry, contract manufacturing has emerged as a strategic and efficient approach for brands looking to bring their culinary visions to life. This article provides an in-depth exploration of how contract manufacturing operates in the food and beverages sector, elucidating the intricacies of the process, elucidating the reasons behind the preference for this model, and examining its global impact.
Understanding the Contract Manufacturing Process in Food & Beverages:
1. Strategic Partnership Formation:
Contract manufacturing in the food and beverages industry begins with the establishment of a strategic partnership between a brand and a specialized manufacturing facility. This facility, often equipped with state-of-the-art technology and adherence to industry regulations, becomes the extended arm of the brand’s production capabilities.
2. Product Development and Formulation:
The collaboration involves extensive discussions on product development, where the brand communicates its vision, flavor profiles, and quality standards to the contract manufacturer. Together, they fine-tune formulations to meet not only the brand’s specifications but also regulatory and safety standards.
3. Raw Material Sourcing:
Contract manufacturers take charge of sourcing raw materials required for production. This can range from sourcing locally for freshness and sustainability to procuring globally for unique ingredients. The meticulous selection of ingredients is crucial to ensuring the desired taste, texture, and quality of the final product.
4. Production and Quality Control:
The actual production process is where the contract manufacturer flexes its operational muscles. From blending ingredients to packaging, every step is executed with precision. Rigorous quality control measures are in place to guarantee that each batch meets the brand’s specifications and regulatory requirements.
5. Packaging and Labeling:
Contract manufacturers often handle the packaging and labeling of products, ensuring compliance with branding guidelines and legal requirements. This includes creating attractive and informative packaging that aligns with the brand’s identity.
6. Storage and Distribution:
Post-production, the finished products are stored in the manufacturing facility’s warehouses before being distributed. Some contract manufacturers also take charge of distribution logistics, streamlining the supply chain for the brand.
Why Food & Beverages Brands Prefer Contract Manufacturing?
1. Cost Efficiency:
Contract manufacturing allows food and beverages brands to benefit from economies of scale. Sharing production facilities with other brands reduces operational costs, making it a financially viable option, especially for startups and small to medium-sized enterprises.
2. Focus on Core Competencies:
By outsourcing manufacturing processes to specialized facilities, brands can focus on their core competencies such as marketing, brand building, and innovation. This strategic outsourcing enhances overall business agility.
3. Access to Expertise and Technology:
Contract manufacturers often boast specialized expertise and advanced technology that may be costly for individual brands to invest in. Collaborating with these facilities grants brands access to cutting-edge capabilities without the burden of ownership.
4. Scalability:
Contract manufacturing allows brands to scale production up or down based on market demand. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in the unpredictable world of the food and beverages industry.
5. Risk Mitigation:
Brands can mitigate risks associated with production, such as equipment breakdowns, regulatory changes, or ingredient shortages, by relying on the expertise and resources of contract manufacturers.
The Global Impact of Contract Manufacturing on Food & Beverages Brands:
Contract manufacturing has had a profound global impact on food and beverages brands, shaping the industry in several ways:

1. Market Expansion:
Contract manufacturing facilitates market expansion for brands by providing a cost-effective means to produce and distribute products in different regions. This is particularly crucial for brands aiming to tap into international markets without establishing dedicated production facilities.
2. Cultural Adaptation:
Brands can adapt their products to local tastes and preferences by collaborating with contract manufacturers in different regions. This customization helps them resonate with diverse consumer bases.
3. Supply Chain Optimization:
The global network of contract manufacturers contributes to the optimization of the supply chain. This interconnectedness enhances the efficiency of production, distribution, and response to market fluctuations.
Challenges in Contract Manufacturing:
While contract manufacturing offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges:
1. Communication Barriers:
Effective communication between brands and contract manufacturers is crucial. Differences in language, time zones, and cultural nuances can lead to misunderstandings, impacting the quality of the end product.

2. Quality Control Consistency:
Maintaining consistent quality across batches can be challenging, especially when working with different contract manufacturers. Brands need robust quality control mechanisms to ensure their standards are met every time.
3. Intellectual Property Concerns:
Protecting intellectual property, including recipes and formulations, poses challenges in contract manufacturing. Clear contractual agreements and legal frameworks are essential to safeguard proprietary information.
Recent Trends in Contract Manufacturing:
1. Clean Label Products:
Brands are increasingly focusing on clean label products, and contract manufacturers are adapting by incorporating natural and organic ingredients, minimizing additives, and emphasizing transparency in labeling.
2. Sustainable Practices:
Sustainability is a growing trend in contract manufacturing. Brands are seeking partners who adopt eco-friendly practices, reduce waste, and prioritize environmental responsibility in the production process.
3. Technological Integration:
The integration of advanced technologies, such as automation and artificial intelligence, is transforming contract manufacturing. This trend enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures precision in production processes.
4. Customization and Personalization:
The demand for customized and personalized food and beverages is on the rise. Contract manufacturers are adapting by offering flexible production capabilities to meet the unique preferences of brands and consumers.
Conclusion:
In the expansive realm of the food and beverages industry, contract manufacturing stands as a dynamic force reshaping how brands bring their culinary creations to the table. The collaborative nature of this model, combined with its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and access to specialized expertise, has positioned it as a strategic choice for brands worldwide. While challenges persist, ongoing trends in sustainability, technological integration, and customization underscore the resilience and adaptability of contract manufacturing in meeting the evolving needs of the industry.







