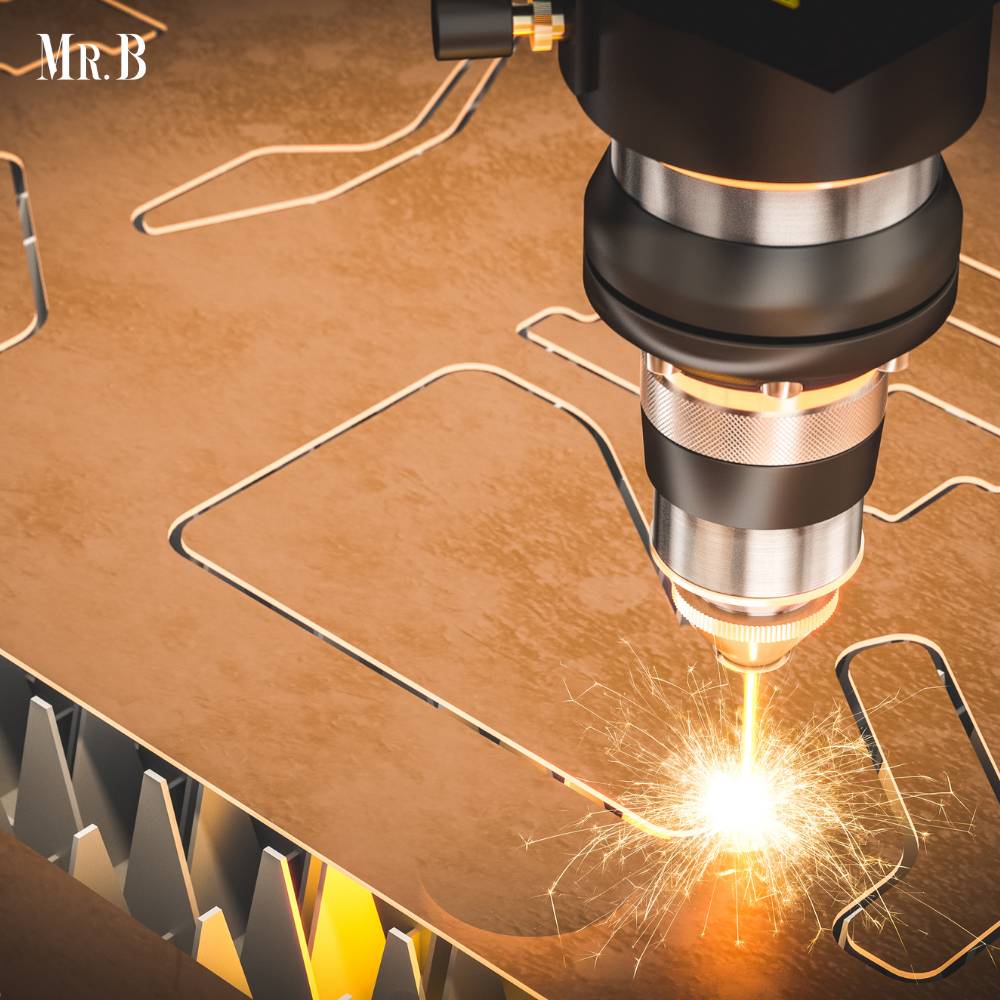
In the realm of manufacturing and engineering, precision machining stands as a cornerstone, seamlessly blending artistry and scientific precision. This article delves into the intricate world of precision machining, exploring its significance, applications, and the advanced technologies driving this field forward.
Understanding the Concept: Precision Machining
Precision machining is a specialized manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into intricate components with unparalleled accuracy. This technique crafts components to incredibly tight tolerances, employing cutting-edge machinery and tools, ensuring high-quality and consistent results.
Applications:
1.Aerospace Industry:
Precision machining plays a pivotal role in crafting components for the aerospace sector, where reliability and accuracy are non-negotiable. From engine components to intricate parts of navigation systems, it ensures optimal performance.
2.Medical Device Manufacturing:
In the medical industry, this machining is indispensable for producing components for various medical devices. From surgical instruments to implantable devices, the accuracy provided by it is critical for patient safety and treatment efficacy.
3.Automotive Manufacturing:
The automotive industry relies heavily on it for the production of engine components, transmission parts, and intricate components that contribute to vehicle performance and safety.
4.Electronics and Technology:
Precision machining is instrumental in the production of components for electronic devices, ensuring the seamless integration of intricate parts in smartphones, computers, and other gadgets.
5.Energy Sector:
Components used in the energy sector, such as turbine blades and specialized fittings, benefit from precision machining, ensuring efficiency and durability in power generation processes.
Technological Advancements:
1.Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining:
It has evolved with the integration of CNC technology, enabling automated and highly precise machining processes. CNC machines follow programmed instructions, resulting in consistent and accurate components.
2.3D Printing in the Machining:
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized it, offering new possibilities for complex geometries and rapid prototyping. This technology complements traditional machining processes, expanding the capabilities of precision manufacturing.
3.Advanced Materials:
It is adapting to the use of advanced materials, including alloys and composites, which demand specialized machining techniques. Modern machining processes are equipped to handle these materials, ensuring precision and durability.
Benefits:
From aerospace to medical device manufacturing, the benefits of precision machining resonate across sectors, shaping the future of production with its accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability. As industries continue to evolve, the role of it will undoubtedly remain pivotal in driving innovation and excellence. Here are 8 benefits of it:
1.Exceptional Accuracy:
At the core of precision machining lies its unparalleled accuracy. The process ensures that components are manufactured with tight tolerances, guaranteeing consistency and reliability. This precision is crucial in industries where even the slightest deviation can impact overall performance.
2.Enhanced Efficiency:
It maximizes efficiency by optimizing the manufacturing process. The automated nature of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines allows for the swift and precise execution of tasks, reducing production times and minimizing errors.
3.Cost-Effective Production:
Although this machining may initially require a significant investment in technology and skilled labor, the long-term benefits outweigh the costs. The accuracy and efficiency of the process contribute to minimizing material waste and reducing overall production expenses.
4.Versatility in Materials:
It is adaptable to a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, and composites. This versatility makes it an ideal choice for industries working with diverse materials, ensuring that the process can meet the unique demands of each application.
5.Consistent Quality:
Achieving consistent quality is a hallmark of the machining. The automated processes, coupled with stringent quality control measures, result in components that meet or exceed industry standards. This consistency is vital in sectors where reliability is paramount.
6.Complex Geometries:
It excels in creating components with intricate and complex geometries. The advanced capabilities of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines enable the production of detailed and sophisticated parts, expanding design possibilities in various industries.

7.Reduced Manual Labor:
With the integration of CNC technology, the machining minimizes the need for extensive manual labor. This not only enhances worker safety but also allows skilled operators to focus on tasks that require critical thinking and problem-solving, further improving overall productivity.
8.Swift Prototyping and Shorter Lead Times:
It facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling manufacturers to test and iterate designs quickly. This agility in the development phase translates to shorter lead times for production, providing businesses with a competitive edge in responding to market demands.
FAQs:
Q.1 What is precision machining?
It is a manufacturing process that utilizes specialized machinery to produce highly accurate and intricate components with tight tolerances, ensuring reliability and quality.
Q.2 How does CNC machining contribute to the machining?
CNC machining automates the machining process using computer-controlled systems, allowing for precise and consistent results, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of it.
Q.3 What industries benefit from precision machining?
It is crucial in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, automotive, electronics, and the energy sector, where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Q.4 How has 3D printing impacted precision machining?
3D printing has expanded the capabilities of the machining by allowing for the production of complex geometries and rapid prototyping, complementing traditional machining processes.
Q.5 Why is this machining essential in the manufacturing sector?
It ensures the production of high-quality components with tight tolerances, contributing to the efficiency, reliability, and safety of various industries in the manufacturing sector.
Conclusion:
Precision machining stands at the forefront of modern manufacturing, weaving together technology, accuracy, and innovation. As industries continue to demand components with ever-increasing precision, the evolution of it remains crucial in shaping the future of manufacturing and engineering.







