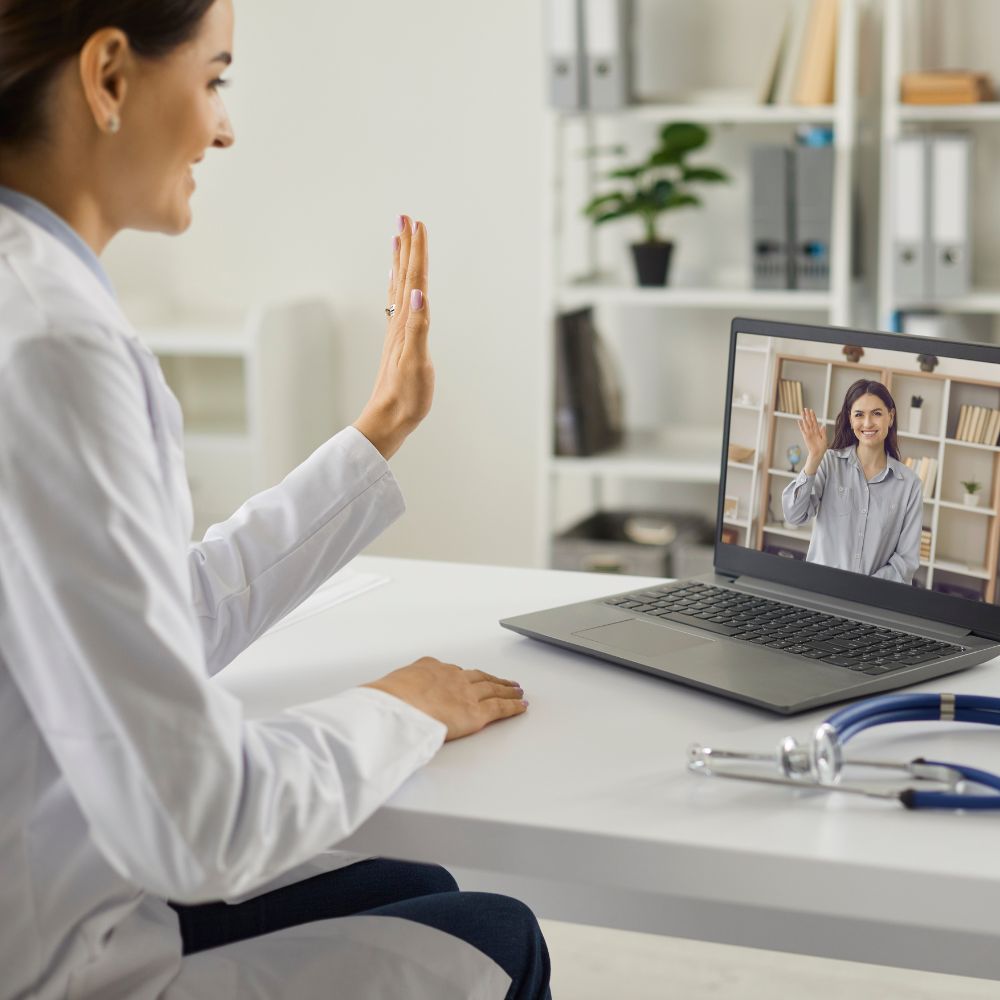
In recent years, the healthcare industry has undergone a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements that have made it possible to deliver care beyond traditional clinical settings. One of the most promising developments in this realm is remote patient monitoring (RPM), a technology that allows healthcare providers to monitor and manage patients’ health conditions from a distance. This approach is reshaping how healthcare is delivered, improving patient outcomes, and reducing costs. In this article, we will explore the concept, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
It refers to the use of digital technologies to collect and transmit health data from patients in one location to healthcare providers in a different location for assessment and recommendations. This technology enables continuous monitoring of a patient’s health status, allowing for timely interventions and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
RPM typically involves the use of devices such as wearable sensors, mobile apps, and home monitoring equipment to track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and more. The data collected is then securely transmitted to healthcare providers who can analyze it and make informed decisions about the patient’s care.
The Benefits:
1. Improved Patient Outcomes
One of the most significant advantages is its potential to improve patient outcomes. By continuously monitoring patients’ health conditions, healthcare providers can detect early signs of deterioration and intervene promptly. This proactive approach can prevent complications, reduce hospital readmissions, and enhance overall patient health.
2. Enhanced Patient Engagement
It empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health. With access to their own health data, patients can gain a better understanding of their conditions and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options. This increased engagement can lead to better adherence to treatment plans and improved health outcomes.
3. Cost Savings
It can significantly reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for hospitalizations and emergency room visits. By providing continuous monitoring and early intervention, RPM can help prevent costly complications and reduce the burden on healthcare facilities.
4. Increased Access to Care
For patients in remote or underserved areas, it can provide access to healthcare services that may otherwise be unavailable. RPM eliminates geographical barriers, allowing patients to receive timely care from specialists without the need to travel long distances.
5. Enhanced Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease require ongoing monitoring and management. Remote patient monitoring provides a convenient and efficient way to track these conditions, enabling healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed and prevent complications.
Challenges in Implementing
1. Data Security and Privacy
One of the primary concerns associated with remote patient monitoring is the security and privacy of patient data. The transmission and storage of sensitive health information must comply with stringent regulations to protect patient confidentiality. Healthcare providers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard data from breaches and unauthorized access.
2. Technological Barriers
The successful implementation relies on the availability and reliability of technology. Patients and healthcare providers must have access to appropriate devices and internet connectivity to ensure seamless data transmission. Additionally, some patients may face challenges in using technology, necessitating user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training.
3. Reimbursement and Regulatory Challenges
The reimbursement landscape for remote patient monitoring services is still evolving. Healthcare providers may encounter difficulties in obtaining reimbursement for RPM services, which can hinder widespread adoption. Additionally, regulatory frameworks must keep pace with technological advancements to ensure the safe and effective use of RPM.
4. Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
To maximize the benefits seamless integration with existing healthcare systems is essential. Data collected through RPM must be easily accessible and compatible with electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitate comprehensive patient care.
Remote Patient Monitoring in Practice:
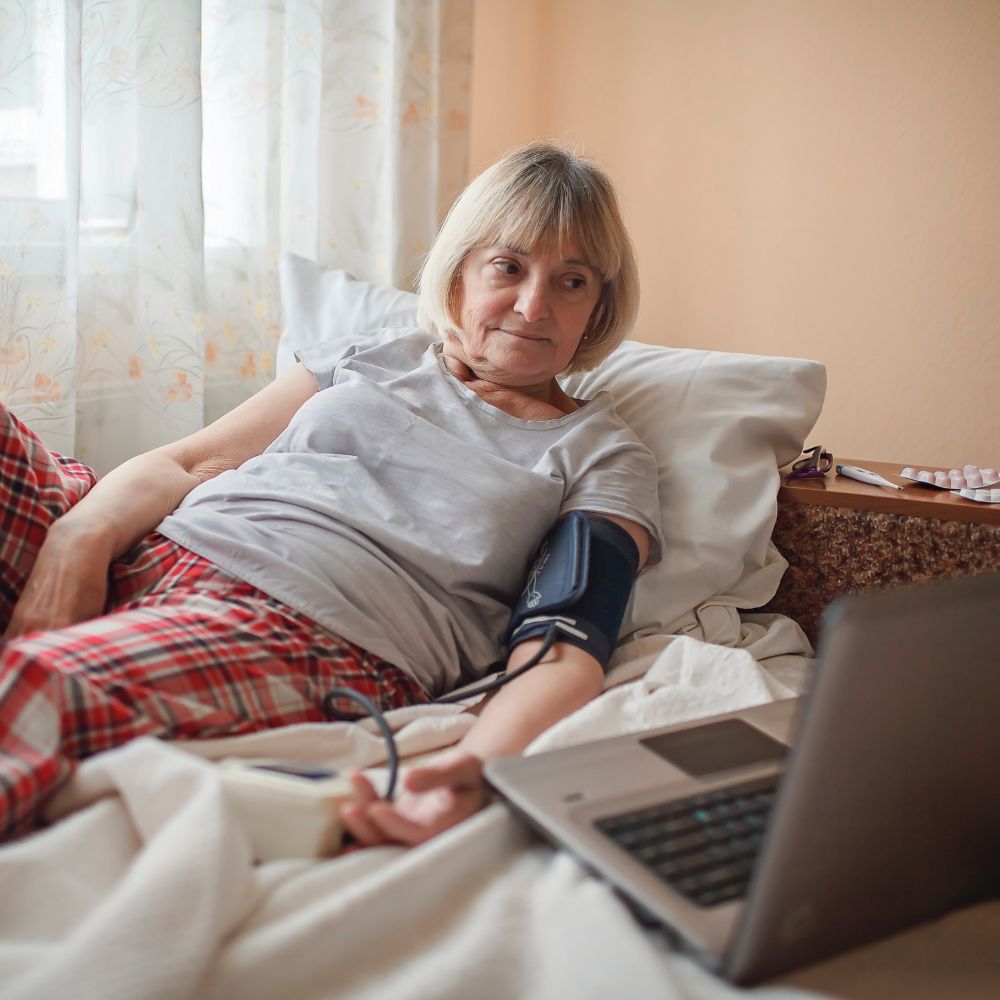

1. Case Study: Managing Chronic Heart Failure
Chronic heart failure is a common and debilitating condition that requires careful management to prevent exacerbations and hospitalizations. It has been shown to improve outcomes for patients with heart failure by enabling continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure.
In one study, patients with heart failure used wearable sensors to monitor their health data, which was transmitted to a centralized platform for analysis. Healthcare providers received real-time alerts if any abnormalities were detected, allowing them to intervene promptly. This proactive approach resulted in a significant reduction in hospital readmissions and improved patient quality of life.
2. Case Study: Diabetes Management
Diabetes is another chronic condition that can benefit from remote patient monitoring. Continuous glucose monitoring systems allow patients to track their blood sugar levels throughout the day, providing valuable insights into their condition. This data can be shared with healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans and prevent complications.
A study involving patients with diabetes who used remote monitoring devices found that they experienced better glycemic control and a reduction in diabetes-related complications. The ability to monitor glucose levels in real time empowered patients to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
The Future of Remote Patient Monitoring
The future is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption across healthcare settings. Several trends are likely to shape the future of RPM:
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to enhance remote patient monitoring by analyzing large volumes of health data and identifying patterns that may indicate a decline in a patient’s condition. AI-powered algorithms can provide predictive insights, enabling healthcare providers to intervene before a critical event occurs.
2. Expansion of Wearable Devices
The proliferation of wearable devices is expected to drive the growth. From smartwatches to biosensors, these devices are becoming more sophisticated, offering a wide range of health monitoring capabilities. As wearable technology becomes more affordable and accessible, more patients will benefit from RPM.
3. Telehealth Integration
Telehealth and remote patient monitoring are complementary technologies that can work together to deliver comprehensive care. By integrating telehealth platforms with RPM, healthcare providers can conduct virtual consultations and follow-ups, ensuring continuity of care and reducing the need for in-person visits.
4. Personalized Medicine
It can facilitate personalized medicine by providing detailed insights into a patient’s unique health profile. Healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans based on individual health data, optimizing outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.
Conclusion
Remote patient monitoring is revolutionizing healthcare delivery by continuously monitoring patients’ health conditions and facilitating timely interventions. This technology offers numerous benefits, including improved patient outcomes, enhanced patient engagement, cost savings, and increased access to care. However, challenges such as data security, technological barriers, reimbursement, and integration with existing systems must be addressed to realize the potential of RPM fully.
As technology continues to evolve, it is poised to become an integral part of healthcare, transforming how care is delivered and improving patients’ lives worldwide. The future of healthcare lies in harnessing the power of technology to provide personalized, efficient, and patient-centered care, and remote patient monitoring is at the forefront of this transformation.







