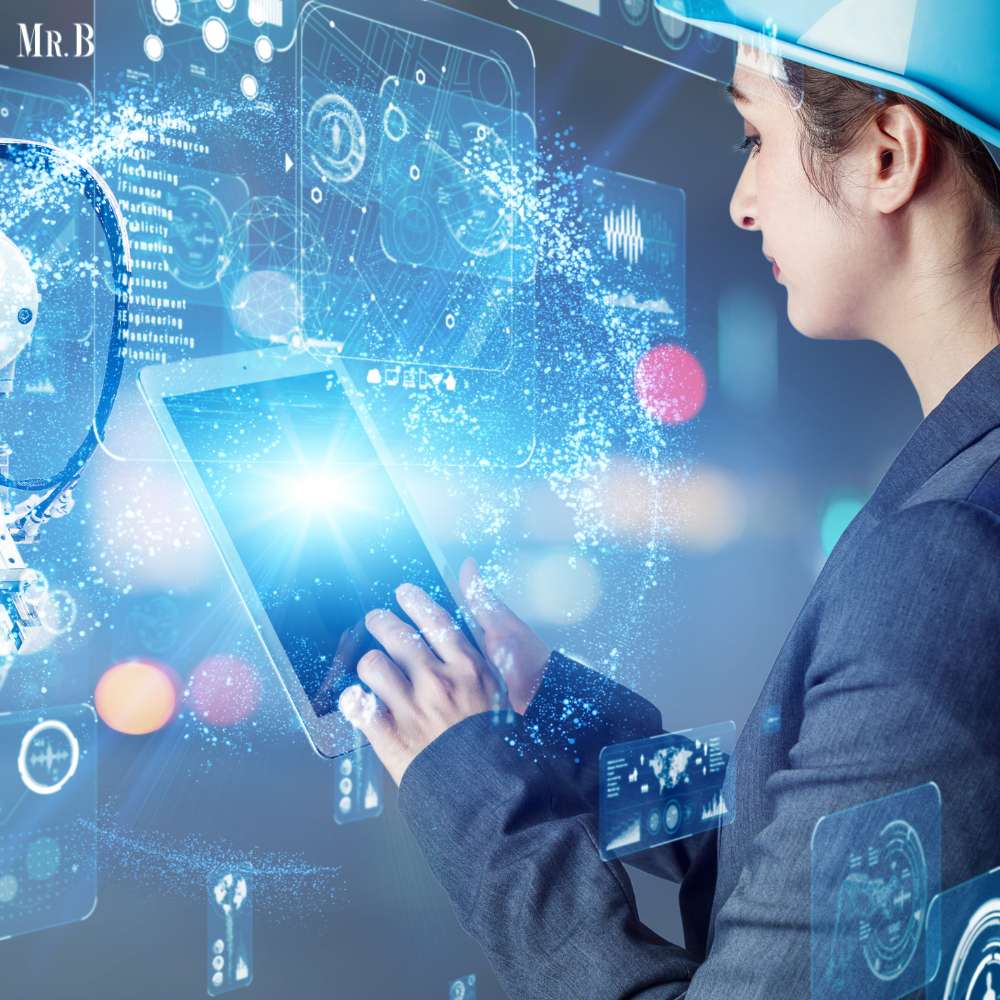
In the manufacturing industry, embracing technological advancements that redefine traditional processes is an integral part that separates one from the competition. One such transformation is the advent of Industry 4.0, a term that’s been making waves across the manufacturing sector. This article explores how Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution is revolutionizing the factory floor, offering insights into the technologies and strategies that are reshaping the landscape.
Understanding Industry 4.0
Before delving into its impact, let’s first grasp what Industry 4.0 is all about. The Fourth Industrial Revolution represents the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. It builds on the progress of previous industrial eras, such as the introduction of mechanization, mass production, and automation.
The core idea behind the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the creation of “smart factories.” These are highly connected and autonomous manufacturing environments where machines, systems, and humans communicate and collaborate seamlessly. The ultimate goal is to enhance efficiency, productivity, and flexibility while minimizing waste.
Key Technologies
Several transformative technologies are driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution on the factory floor. Here are some of the key players:

1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT involves embedding sensors and communication devices into machinery, allowing them to collect and exchange data. This real-time data flow enables manufacturers to monitor the condition of equipment, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
For instance, a machine equipped with IoT sensors can alert operators when it’s time for maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
2. Big Data and Analytics
The massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices need to be harnessed effectively. Big data analytics tools process this data to provide valuable insights. Manufacturers can use these insights to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and identify areas for improvement.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are crucial components of Industry 4.0. They enable machines to learn from data and make intelligent decisions. In manufacturing, AI-powered systems can predict defects, optimize production schedules, and even control robotic arms with precision.
4. Robotics and Automation
Robots have been a part of manufacturing for years, but Industry 4.0 takes their role to new heights. Collaborative robots, or cobots, can work alongside humans safely. They perform repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of production.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are being used for training, maintenance, and design. Workers can receive step-by-step instructions through AR glasses, reducing the need for extensive training. VR is also used for virtual prototyping and designing factory layouts.
Impact on the Factory Floor
Now that we understand the technologies behind the Fourth Industrial Revolution, let’s delve into how they are reshaping the factory floor:
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Efficiency is a cornerstone of manufacturing, and the Fourth Industrial Revolution delivers on this front. With real-time data from IoT sensors and AI-driven insights, manufacturers can optimize production processes to minimize downtime, reduce waste, and increase throughput. This means quicker turnaround times and lower production costs.
2. Improved Quality Control
Quality control is critical in manufacturing, and Industry 4.0 raises the bar. AI-driven quality control systems can detect defects with unmatched precision, ensuring that only high-quality products make it to market. This not only enhances brand reputation but also reduces the costs associated with recalls and rework.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Unplanned downtime can be a significant drain on resources. The Fourth Industrial Revolution’s predictive maintenance capabilities, powered by IoT and AI, can foresee equipment failures before they occur. This allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of machinery.
4. Flexibility and Customization
Modern consumers demand customization, and manufacturers are answering the call. Smart factories can quickly reconfigure production lines to accommodate changing customer preferences. This flexibility allows for the efficient production of small batches or even individualized products, which was previously challenging.
5. Safety and Collaboration
Collaborative robots (cobots) and augmented reality tools enhance workplace safety. Cobots can handle dangerous tasks, while AR glasses provide workers with vital information and guidance, reducing the risk of accidents.

6. Sustainable Manufacturing
The Fourth Industrial Revolution aligns with sustainability goals. Optimized processes reduce energy consumption and waste, making manufacturing more eco-friendly. Additionally, IoT sensors can track resource usage, enabling better resource management and reduced environmental impact.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Fourth Industrial Revolution offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider:
1. Cost: Implementing these technologies requires a significant upfront investment, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
2. Cybersecurity: Increased connectivity also means an increased risk of cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect sensitive data and operations.
3. Skills Gap: Adopting Industry 4.0 requires a workforce with new skills. Manufacturers need to invest in training and upskilling their employees.
4. Data Privacy: Collecting vast amounts of data raises concerns about data privacy and how it’s handled, stored, and shared.
Summing UP
Today, Industry 4.0 is a transformative force that is revolutionizing the factory floor. By integrating IoT, big data, AI, robotics, and other technologies, manufacturers can achieve enhanced efficiency, improved quality control, predictive maintenance, and sustainability.
However, it’s essential to navigate the challenges wisely, invest in the right technology, and prioritize workforce development to fully harness the potential of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. As this revolution continues to unfold, those who adapt stand to gain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving world of manufacturing.







